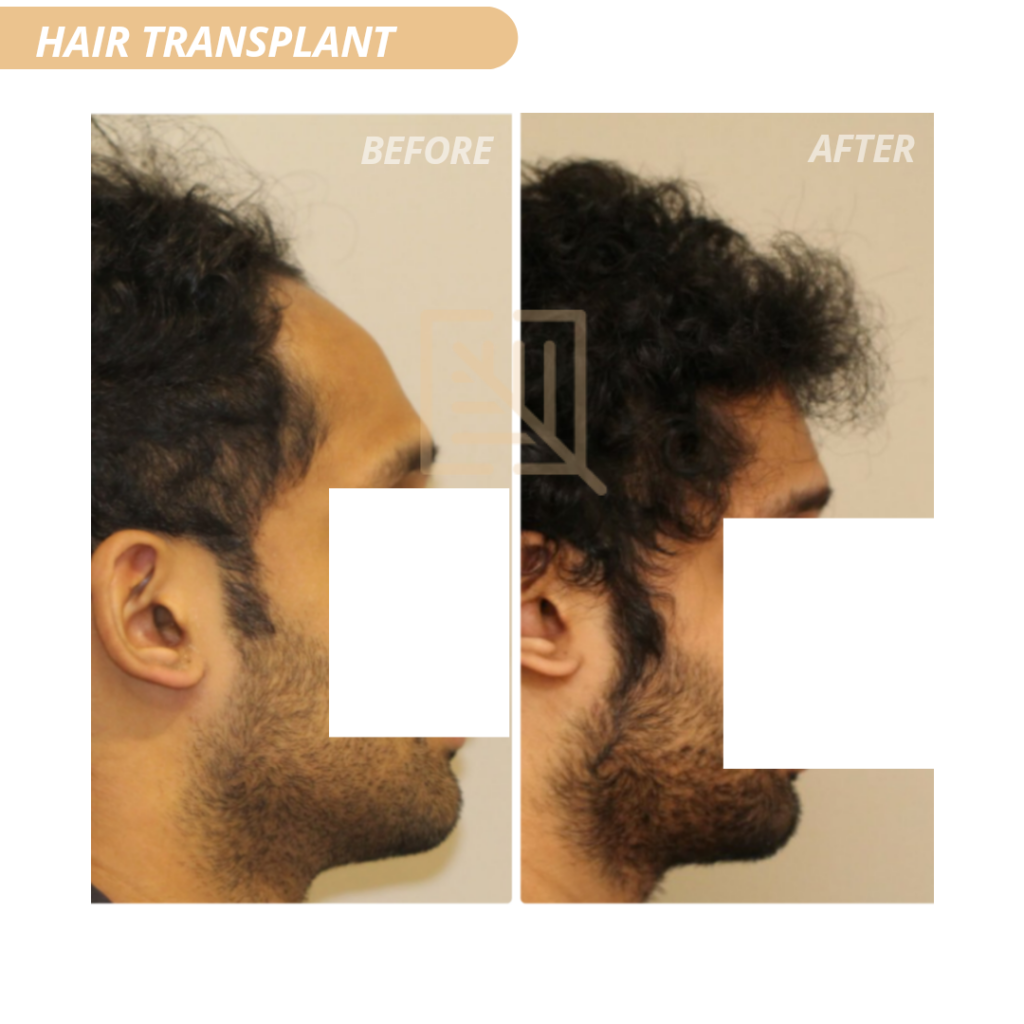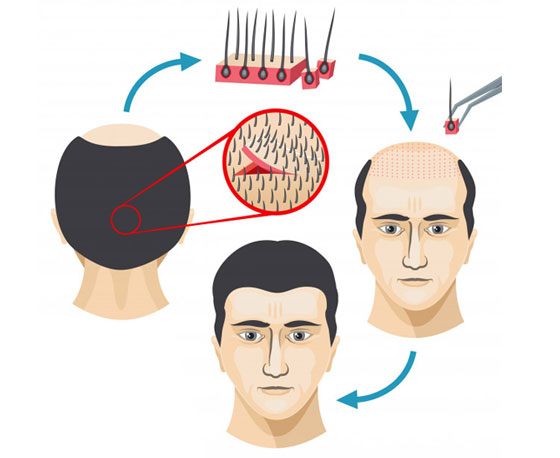
Hair transplantation is the process of surgically removing hair from one part of the body or donor site and transplanting it to a bald area/ recipient site. It is most commonly used for treating androgenetic alopecia (AGA) also known as male pattern baldness. Most common site selected as a donor area is the strip of hair at the back of the head (occipital region).
About the procedure
Hair transplantation is a day care procedure that is done under local anesthesia. The scalp hair is trimmed and the donor and recipient sites are marked.
There are two basic techniques of harvesting from donor area- follicular unit transplant (FUT)/strip method and follicular unit extraction (FUE). The latest technique is FUE wherein micro-punches of 0.7 – 0.8 mm size are used to dissect the follicular units. This ensures a negligible scar at the site of harvest. Each hair follicle usually contains 2-4 hairs which are dissected and implanted into slits which are made in the recipient area. Time taken for the procedure is around 4-6 hours depending on the number of grafts used.
Recovery and healing
Patient can resume his daily activities from the very next day of surgery. Post op dressing is removed after 36 hours following which washing with a mild baby shampoo is advised. Antibiotics and pain medications are prescribed to ensure patient comfort.
Risks
With the advent of the latest FUE technique, risk of side effects has reduced considerably compared to the FUT technique. Most commonly observed complaints are-
- Post-operative pain (which can be controlled with use of analgesic medications)
- Oozing and minor bleeding from the donor site
- Post-operative forehead and eyelid edema which is more commonly seen in elderly individuals with lax skin. It can be minimized by use of a pressure bandage and lying down.
- Crusts around the transplanted grafts, which can be gently removed with shampoo and saline soaks.
- Post-operative effluvium/ hair loss from donor site, which resolves spontaneously
Some of the rarer side effects that are seen are :
- Folliculitis of the donor site (if proper asepsis is not followed during the procedure)
- Scarring at the donor site due to overharvesting